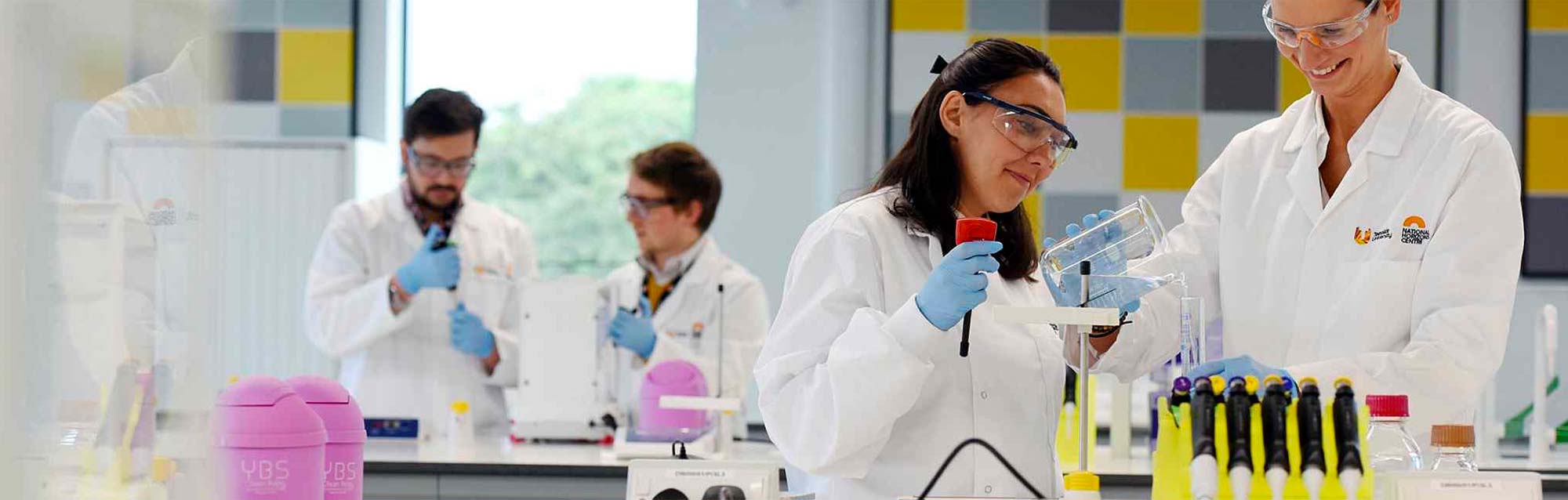
Course overview
You undertake a broad range of clinical laboratory investigations in pathology, immunology and infectious disease control.
Professional accreditation for this degree comes from by the Institute of Biomedical Science, giving you the opportunity to train as a professional biomedical scientist. As a graduate you can pursue a career as an accredited biomedical scientist or a professional in the biomedical sector.
You explore fundamental concepts of human anatomy and physiology, cell biology, pathology, biochemistry, genetics, immunology and microbiology. Employability skills include good laboratory practice, COSHH assessments, health and safety policies, the Human Tissue Act, quality assurance, and transferable skills including verbal and poster presentations, written reports, independent research and teamworking. You experience key clinical laboratory skills from accredited biomedical scientists from local hospital trusts and industrial partners.
You study at our Middlesbrough campus, but during your degree you could gain valuable experience at the National Horizons Centre at our Darlington campus. This £22.3m purpose-built biosciences research, education and training facility is a focal point for the growing regional biosciences community.
This course includes a foundation year - ideal if you need additional preparation or if you don't have sufficient grades to join Year 1 of a degree.
Top reasons to study this course
- You join a supportive, expanding, thriving and diverse biomedical science community of staff and students.
- As a graduate you can train as an accredited biomedical scientist.
- Staff expertise in biomedical science includes academics and practitioners from local hospital trusts and biotechnology companies.
- You will have the opportunity to conduct a research project at our £22.3m National Horizons Centre.
- Lectures and lab sessions are delivered by internationally-recognised researchers with expertise in disciplines including cancer, dementia, asthma and infectious diseases.
- Teesside is ranked 6th out of 64 institutions for Biomedical Science in the Guardian University Guide 2024. (122 institutions participated, tees.ac.uk/source).
Study this course and you may be eligible for the Professor Leni Oglesby Transformation Scholarship or Cleveland Scientific Institution Scholarship.
Course details
Course structure
Foundation year core modules
What is big data? How is it made and how do we make sense of it? Discover how data is created, consider the ethical implications of using it and begin your journey accessing it. You explore its use in society and the role it plays in community relationships, from uncovering criminal networks and tracking disease outbreaks to developing a deeper understanding of our ecology. You understand how search engines collate and store the data needed to make predictions, enhance decision making, or to better understand society’s needs. You learn the impact big data has and the challenges it presents.
This is a 20-credit module.
Chemical Science and the Environment
Chemistry is the study of the structure, properties and reactivity of elements and compounds and plays a key role in physical, life and applied sciences. You are introduced to the fundamental concepts of the application of chemistry. You examine the structure of the atom, the periodic table, chemical bonding and chemical reactivity. Learn about environmental science, biogeochemistry, pollution, green chemistry and climate change.
This is a 20-credit module.
Experimental Methods for Life Science
Explore your academic interests in a practical setting, learning how to work safely and properly document your work. If you’re interested in biology, you investigate the basics of microscopy and the handling of microorganisms. If your preference is food sciences, you begin to look at the safe handling of food. And if you’re interested in chemistry, you begin to use volumetric glassware and investigate acid-base titrations.
This is a 20-credit module.
Team up with your coursemates to find out how science can help address some of the biggest issues facing society today. You explore health and wellbeing, resilient and secure societies, digital and creative economy, sustainable environments, and learning for the 21st century.
This is a 20-credit module.
You explore the diversity of life on earth and the concept of evolution. You discuss Darwin’s theory to demonstrate relationships between species, the principles of taxonomy and speciation, and how they relate to the evolutionary tree.
Physiological processes, cellular organisation, homeostasis, metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli and adaptation - these are the hallmarks of living organisms and equip diverse species to survive and thrive. You complete an in-depth analysis of a number of organisms to examine and compare the strategies they use to thrive and appreciate how evolution has led to divergent life forms. You normally take part in a field visit to a local site to examine biodiversity and the natural world.
This is a 20-credit module.
You focus on life sciences from a human perspective, while developing an understanding of human biology to explore the role of different but interconnected life science disciplines in modern life. You consider the major human body systems (cardiovascular, respiratory, excretory, endocrine, nervous, digestive, skeletal and reproductive) to appreciate how this knowledge is relevant to issues in health, disease and modern society.
This is a 20-credit module.
Year 1 core modules
Gain basic knowledge of human anatomy and an understanding of the mechanisms associated with control and regulation of the physiological processes of the major organ system. Homeostasis is the key theme throughout the module, as you explore interrelationships between human functions and the organisational hierarchy to develop and increase your understanding of how the body functions. You also study the construction of biological profiles for human identification including sex, age at death, stature determination and biological affinity. This knowledge is used in the context of identification and recovery of human remains, the regulatory aspect of handing human remains and ethical issues related to human tissue research.
This is a 20-credit module.
Biochemistry and Chemical Science
Study the key principles of biochemistry, including the structure of the atom, chemical bonding and the forces that operate between molecules, chemical reactions and biological pathways. Investigate the chemistry of carbon and why this element is capable of forming the complex three-dimensional molecules that make life possible. Crucial groups of biological molecules are studied in detail, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
This is a 20-credit module.
At a cellular level, you develop your understanding of biological processes. You explore the common features and immense diversity of form and function displayed by cells of organisms. You examine eukaryotic cell architecture and function with a molecular and mammalian focus and learn about cell division, the cell cycle, genetic organisation of cells, DNA replication and gene expression.
This is a 20-credit module.
Practical skills are essential to the role of a biomedical scientist working in a hospital lab environment. You are introduced to the basic principles of lab skills including good lab practice, accurate recording of experimental data and competency in basic lab procedures. You also cover a range of techniques used in handling and analysing clinical samples including point-of-care testing - here you learn to identify and report on blood types using common procedures in a biomedical haematology and transfusion lab.
This is a 20-credit module.
Microbiology is crucial in many aspects of life science. You study the fundamental aspects of microbiology, learn key practical skills and theoretical concepts covering a range of microorganisms including bacteria, viruses and eukaryotic microbes. You focus on microbial cell structure and function, microbial growth, microbial diversity, the importance of microbes in the environment, industry and human health. And you benefit from a strong practical element that introduces key microbiological lab skills.
This is a 20-credit module.
You gain an overview of normal histology and cytology of major organs and systems of the human body and molecular and cellular factors underpinning the pathology of common diseases. You examine the causes, mechanisms and extent of disease, as well as adaptations to injury, such as apoptosis and necrosis (death of living cells or tissues), autophagy, inflammation, wound healing and neoplasia (abnormal new growth of cells).
This is a 20-credit module.
Year 2 core modules
Clinical pharmacology encompasses all aspects of the relationship between drugs and humans. It is a diverse discipline that both sustains and advances best healthcare. You explore the nature of drugs as chemicals, which interact with cellular mechanisms at the molecular, systemic and behavioural level. Focus is on the treatment and prevention of disease and you consider the nature of adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals within living systems.
This is a 20-credit module.
Diagnostic and Experimental Pathology
Explore the various techniques involved in a biomedical laboratory to help identify the cause of disease. Procedures involved in the preparation, processing and staining of tissue for use in disease diagnostics and experimental research are introduced. Cellular pathology techniques such as microtomy, microscopy, staining and immunohistochemistry are examined in relation to alterations in cellular, tissue and organ function in different diseases.
This is a 20-credit module.
From fertilisation to infancy, through puberty and into adulthood, you take a journey through your own life. You also examine what happens when the human reproductive system doesn’t work properly, and how advances in reproductive medicine can help.
This is a 20-credit module.
Human Metabolism and Clinical Biochemistry
Gain an understanding of the human metabolism, endocrinology and clinical biochemistry. Examine metabolism, the chemical processes that occurs in living organisms, in the context of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, cellular respiration and metabolism of drugs. Discuss endocrinology and review the mechanisms underpinning hormone action, the roles of second messengers and endocrine system disorders. Enzyme kinetics and enzyme regulation is a significant topic. Explore the methods used for collecting, measuring and analysing clinical samples in the biomedical lab. Learn the principles and applications of clinical biochemistry investigations used in screening, diagnosing, treating and monitoring disease.
This is a 20-credit module.
You gain a solid foundation in immunology and explore the immune system’s role in protecting against microorganisms and maintaining human health. Examine the functional organisation of the immune system, the immune cells and chemical mediators, antibodies, and cellular processes related to the innate and adaptive immune responses.
This is a 20-credit module.
Molecular Biology and Bioinformatics
You study a range of modern molecular biology concepts and techniques. And you address general molecular biology and experimental techniques, key to the discipline for applications such as the production of recombinant proteins, DNA sequencing and functional gene measurement. The new age of molecular biology is underpinned by gene/genome sequencing, sequence analysis and sequence manipulation. You gain a thorough introduction to the principles of sequence analysis and how these techniques have revolutionised all areas of molecular biology. Particular attention is paid to the technique of polymerasechain reaction (PVR). And you examine informatics concepts, with a focus on visualising and analysing DNA sequence data, as well as basic molecular data analysis. A series of lab sessions introduce the basic techniques that lie at the heart of modern molecular biology such as DNA purification, PCR, restriction digestion, nucleic acid analysis through agarose gels, and sequencing - these are key to industrial biotechnology as well as research science.
This is a 20-credit module.
Final-year core modules
Explore the application of methods for the diagnosis and management of disease as well as the function and dysfunction of systems, organs and tissues by the measurement of biochemical biomarkers. Investigate modern analytical techniques used for the measurement of biochemical markers including the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of disease such as liver and kidney function tests. You are also introduced to therapeutic drug monitoring methods, including those used to investigate drug abuse.
This is a 20-credit module.
You are introduced to genetic disorders, including chromosomal abnormalities, single gene disorders and birth defects with a genetic component, and learn to apply genetics knowledge to disorders seen in patients. Examine current and new techniques such as Next Generation Sequencing and understand advances in the NHS analysis of genetic disorders. Explore the ethics involved in whole genome sequencing and screening for genetic disorders.
This is a 20-credit module.
Clinical Haematology and Transfusion Science
Study the origin and creation of different types of blood cells (red, white, platelets), the roles of these in normal function, and how they are defective in blood disorders, including blood cancers. Learn about blood groups, antibodies, and other important considerations in transfusion as well as transplantation. Coagulation and associated disorders will also be covered. Train in preparing blood films and identifying disorders, blood groups and antibodies in blood samples, and recognising which blood can be donated to who.
This is a 20-credit module.
You examine key human pathogens with a clear emphasis on the subversion of host cells and causation of disease. You explore underlying molecular mechanisms, diagnosis, treatment and overall impact of many key pathogens. You gain an insight into how humans interact with a variety of non-pathogenic microorganisms and how they affect human health.
This is a 20-credit module.
You complete an in-depth, independent investigation into a specialist aspect of your field of study. You bring together a range of practical and academic skills developed in previous study, including analysing and critically evaluating data and a critical reflection on the potential risks, and moral and ethical issues. You are supported by a research supervisor who helps you develop and complete your research project.
This is a 40-credit module.
Modules offered may vary.
How you learn
This course aims to produce graduates who are competent in a range of knowledge, understanding, experience and practical skills appropriate to biomedical science.
You learn through a range of teaching and learning methods including:
- lectures
- tutorials
- seminars and workshops (including oral presentations and poster sessions)
- laboratory work
- computer laboratory-based sessions
- group projects
- research projects.
The course provides a number of contact teaching and assessment hours, but you are also expected to spend time on your own - self-study time - to review lecture notes, prepare coursework assignments, work on projects and revise for assessments. Each year of full-time study consists of modules totalling 120 credits and each unit of credit corresponds to 10 hours of learning and assessment (contact hours plus self-study hours). So, during one year of full-time study you can expect to have 1,200 hours of learning and assessment
Each programme and module is supported by a specific virtual learning environment (VLE) site.
How you are assessed
You may be assessed through:
- formal exams including 'unseen' exams
- laboratory reports
- computer-based assessments
- problem-solving exercises
- data interpretation exercises
- critical analysis of case studies
- oral presentations and technical interviews
- essays, literature surveys, evaluations and summaries
- collaborative project work
- preparation and display of posters
- planning, conduct and reporting of project work
You will be provided with an assessment schedule providing details of the submission deadlines for summative assessments.
Our Disability Services team provide an inclusive and empowering learning environment and have specialist staff to support disabled students access any additional tailored resources needed. If you have a specific learning difficulty, mental health condition, autism, sensory impairment, chronic health condition or any other disability please contact a Disability Services as early as possible.
Find out more about our disability services
Find out more about financial support
Find out more about our course related costs
Entry requirements
Entry requirements
Any Level 3 subject is acceptable for entry to this course.
Normally entry qualifications can be accumulated from:
• any combination of Level 3 qualifications (for example, A/AS levels, BTEC Certificates/Diplomas, Access to Higher Education courses)
• High School Certificate or Diploma with good grades completed after at least 12 years of primary and secondary education
English language and mathematics requirements
Normally, evidence of English language and mathematical skills equivalent to at least GCSE grade 4 is required. We consider a wide range of English and maths qualifications alternative to GCSEs. Please contact our admissions staff for advice.
Non-EU international students who need a student visa to study in the UK should check our web pages on UKVI-compliant English language requirements. The University also provides pre-sessional English language courses if you do not meet the minimum English language requirement.
Applicant Days
If you receive an offer to study with us you may be invited to attend one of our Applicant Days. This is a great opportunity to learn more about studying at Teesside by exploring our campus, seeing our excellent facilities, meeting staff and students, and finding out more about your course.
The Applicant Day provides you with information, guidance and advice to help you make the right choice. Even if you have attended an Open Day we encourage you to attend the Applicant Day - we are confident you will find your visit a useful experience.
Alternative progression routes
If you are not eligible to join this course directly then we may be able to help you prepare for admission by studying appropriate pre-degree Summer University modules.
Please contact us to discuss the alternative progression routes available to you.
For general information please see our overview of entry requirements
International applicants can find out what qualifications they need by visiting Your Country
You can gain considerable knowledge from work, volunteering and life. Under recognition of prior learning (RPL) you may be awarded credit for this which can be credited towards the course you want to study.
Find out more about RPL
Employability
Career opportunities
The biomedical science degree gives you a strong foundation of knowledge in a diverse range of topics, presenting many career choices, including certified biomedical scientist, healthcare scientist or laboratory technician.
Opportunities to pursue a career in medicine or other clinical disciplines, such as pharmacy or as a physician associate are also open to you. Biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries welcome biomedical science graduates in research and development, quality assurance and sales. Publishing companies and the specialist press may also employ biomedical sciences graduates as writers or editors.
You may wish to continue your education by studying for a Master of Science (MSc), Master of Research (MRes) or Doctor of Philosophy (PhD).
Information for international applicants
Qualifications
International applicants - find out what qualifications you need by selecting your country below.
Select your country:
Useful information
Visit our international pages for useful information for non-UK students and applicants.